
Stainless Steel 304/304L Forged Fittings are critical components in various piping systems, known for their robustness, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. They are manufactured using a forging process, which involves shaping heated steel by hammering or pressing, resulting in a dense and strong product with excellent mechanical properties.
Stainless steel forged fittings are pipe fittings forged from stainless steel round bars or billets, and have excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and high pressure resistance. According to different uses and connection methods, stainless steel forged pipe fittings can be divided into many types, such as elbows, tees, crosses, pipe clamps, pipe caps, etc. In today’s industrial field, stainless steel forged pipe fittings have become an important part of fluid transportation systems. As a high-quality, high-performance pipe fittings, stainless steel forged pipe fittings have been widely used in petroleum, chemical, natural gas, refrigeration and other industries.
Manufacturing Methods
Depending on the specific type and requirements of the pipe fitting, forged fittings are primarily manufactured using die forging, open-die forging (free forging), and machining processes. Conventional die forging methods often result in significant flash (excess material), leading to material waste. To reduce material consumption, some fitting manufacturers have started adopting flashless forming processes, achieving good results. This section mainly introduces the processes for manufacturing pipe fittings using die forging, open-die forging, and machining.
① Die Forging
For small-sized fittings with relatively complex shapes, such as socket-weld and threaded tees, crosses, and elbows, die forging should be used.
The raw material (billet) used for die forging should be rolled stock, such as bars, thick-walled pipes, or plates. When steel ingots are used as raw material, they should first be rolled into bars or pre-forged before being used as die forging billets to eliminate defects like segregation and looseness within the ingot.
After heating, the billet is placed into a die and forged (depending on the situation, it might undergo preliminary forging before final die forging). The pressure causes the metal to flow and fill the die cavity. If the forged blank has flash, an additional step of trimming off the excess material is required to complete the entire die forging process.
② Open-Die Forging (Free Forging)
For pipe fittings with special shapes or those unsuitable for die forging, open-die forging can be used. Open-die forging should produce the general shape of the fitting; for example, a tee should have its branch pipe section forged out.
③ Machining
For certain cylindrical-shaped fittings, such as double-socket couplings and unions, they can be directly machined from bar stock or thick-walled pipes. During machining, the metal material’s grain flow should be approximately parallel to the fitting’s axial direction. Tees, crosses, and elbow-type fittings must not be directly machined from bar stock.
Stainless Steel 304 / 304L Forged Fittings Specification
Specifications : ASTM A182 / ASME SA182
Standard : ASME B16.11, MSS-SP-79, MSS-SP-83, MSS-SP-95, MSS-SP-97, BS3799
Size : 1/8″ NB to 4″ NB
Type : Socket weld Fittings, Threaded Fittings
Rating Pressure : Threaded End – 2000 /3000/ 6000 LBS. Socket-weld End – 3000 / 6000/ 9000 LBS.
ASTM A182 F304/304L Chemical Composition
| CHEMICAL | LIMITS | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | N |
| ASTM A182 F304 | MIN | 8.0 | 18.0 | |||||||
| MAX | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 11.0 | 20.0 | 0.10 | ||
| ASTM A182 F304L | MIN | 8.00 | 18.00 | |||||||
| MAX | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.00 | 13.00 | 20.00 | 0.10 |
ASTM A182 F304/304L Mechanical Property
| MATERIAL | T.S (MPA) | Y.S (MPA) | EL % | R/A % |
| ASTM A182 F304 | 515 min | 205 min | 30 min | 50 min |
| ASTM A182 F304L | 485 min | 170 min | 30 min | 50 min |
Types of Stainless Steel 304/304L Forged Fittings
Forged fittings are primarily categorized by their connection method into two main types: Threaded Fittings and Socket Weld Fittings.
These two connection methods determine how the fittings are installed and connected within a piping system, which in turn dictates their respective application scenarios, pressure ratings, and specific advantages and disadvantages.
Socket Weld (SW) Fittings:
Characteristics: The fitting has an internal bore (socket) into which the pipe is inserted. The connection is then made by a fillet weld on the exterior of the fitting. This means the weld is outside the pipe, preventing it from affecting the pipe’s inner diameter.
Applications: Suitable for small-bore, high-pressure, high-temperature piping systems, especially those where a smooth internal wall is not strictly required, or where internal corrosion or scaling needs to be prevented (since the weld is external). Commonly used in the chemical, petroleum, and power industries.
Pressure Ratings: Typically available in Class 3000 LBS, 6000 LBS, 9000 LBS, etc.
Threaded (THD / Screwed) Fittings:
Characteristics: The fitting has internal or external threads (usually NPT or BSPT standards) that connect to the pipe via a threaded connection.
Applications: Suitable for small-bore, medium-to-low pressure, non-critical piping systems. They are easy to install and disassemble, requiring no welding. Commonly used in instrumentation lines, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems.
Pressure Ratings: Typically available in Class 2000 LBS, 3000 LBS, 6000 LBS, etc.
ASTM A182 F304 Forged Fittings Available Types & Shapes
| Forged Stainless Steel 304L Pipe Fittings | ASME SA182M F304L Forged Fittings |
| Stainless Steel 304 Forged Pipe Fittings | Threaded Elbow |
| Socket Weld Cap | Threaded Tee |
| Socket Weld Elbow | Threaded Cross |
| Socket Weld Tee | Threaded Coupling |
| Socket Weld Cross | Threaded Cap |
| Socket Weld Coupling | Threaded Union |
| Socket Weld Union | Threaded Nipple |
| ASTM A182 F304L Reducing Tee | Threaded Hex Nipple |
| A182 SS 304 Hex Nipples | Threaded Swage Nipple |
| Stainless Steel UNS S30400 Socket Weld 90 Deg Elbow | Threaded Plug |
| ASTM A182 SS 304 Screwed Hex Plug | Threaded Bushing |
Stainless Steel Threaded Fittings Dimensions
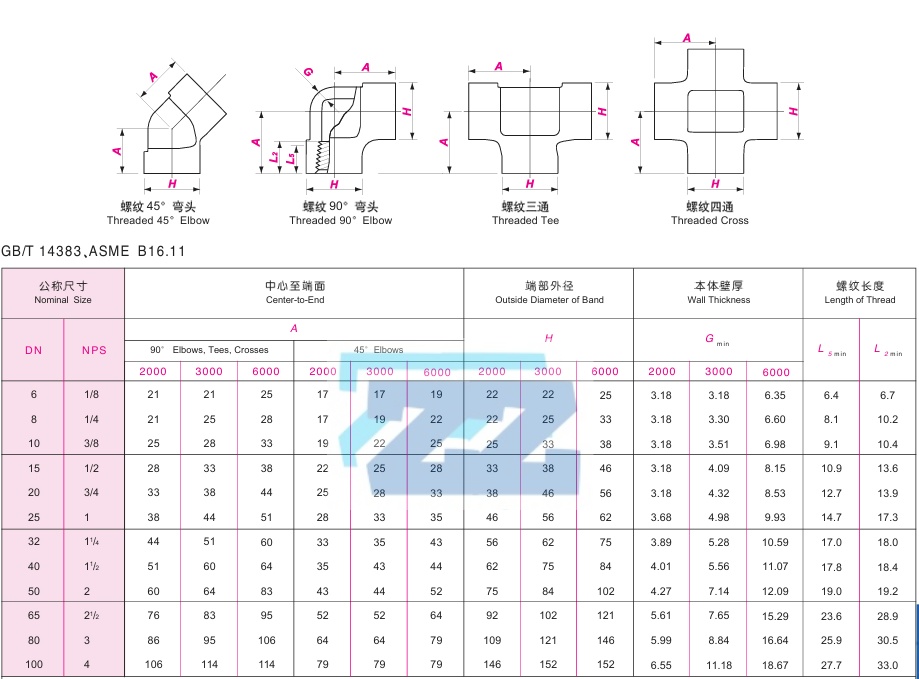
Stainless Steel Socket Weld Fittings Dimensions
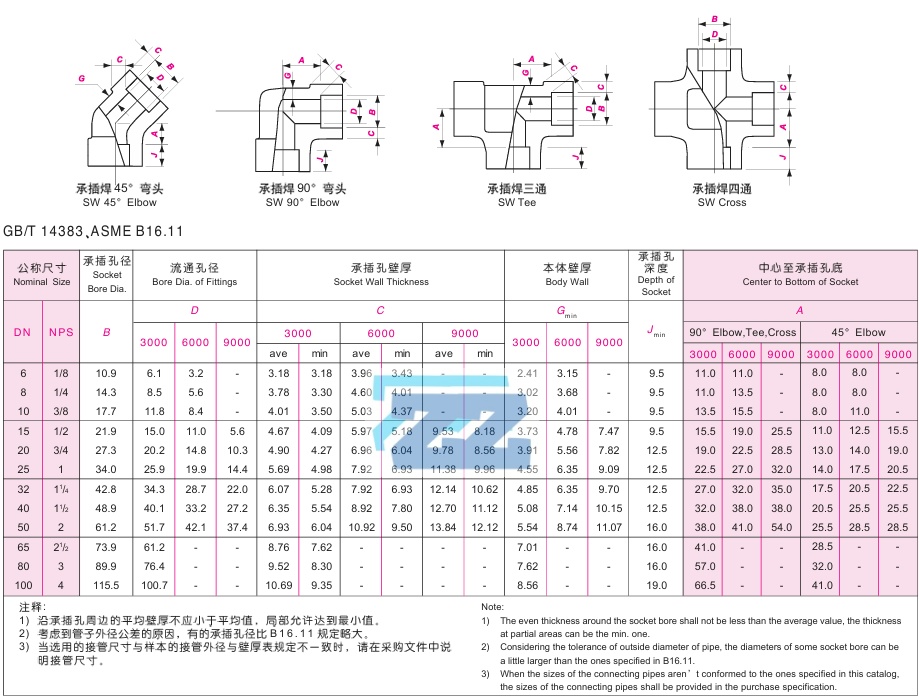
Stainless Steel 304 vs. 304L Grades
Both 304 and 304L are austenitic stainless steels and are part of the “18/8” family (approximately 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel). They offer excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and weldability. The primary difference lies in their carbon content:
Stainless Steel 304 (UNS S30400):
– Contains a maximum carbon content of 0.08%.
– Offers good general corrosion resistance and strength.
– However, during welding, the higher carbon content can lead to carbide precipitation in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), making it susceptible to intergranular corrosion in aggressive environments.
Stainless Steel 304L (UNS S30403):
– “L” stands for “Low Carbon,” with a maximum carbon content of 0.03%.
– This lower carbon content significantly reduces the risk of carbide precipitation during welding, making it highly resistant to intergranular corrosion in the “as-welded” condition.
– It’s the preferred choice for applications where welding is required and where the component will be exposed to corrosive environments without post-weld annealing.
– Due to the lower carbon, 304L has slightly lower mechanical properties (tensile and yield strength) compared to 304, but its improved weldability and corrosion resistance often outweigh this.
Applications of Stainless Steel 304/304L Forged Fittings
Chemical and Petrochemical Industries
Oil and Gas Industry
Food Processing and Pharmaceutical Industries
Power Generation
Water Treatment and Wastewater Facilities
Pulp and Paper Manufacturing
Marine Engineering
General Industrial Applications
Latest News
- 04 3 月 2026Marking Rules for ASME B16 & B36 Piping ProductsASME standards are the most widely used specifications […]...
- 26 2 月 2026ASME B18.2.1-2012 – The Active StandardASME B18.2.1-2012 is the latest active version of […]...
- 24 2 月 2026EN 1092-1 Loose Plate Flange Type 04What is EN 1092-1 Loose Plate Flange Type 04? EN 1092-1 […]...
